Introduction
Google Sheets offers powerful tools for text manipulation and conditional formatting, enabling users to clean, format, and analyse data efficiently. In this article, we will explore various text manipulation techniques, including the use of functions such as CASE, LEFT, MID, RIGHT, CONCATENATE, and TEXTJOIN, as well as the application of conditional formatting.
Why is Text Manipulation and Conditional Formatting Important?
Text manipulation and conditional formatting are crucial for organising, analysing, and visualising data. By transforming and highlighting data, you can enhance readability, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting allows you to automatically apply formatting—such as colours, icons, and data bars—based on the contents of cells. This feature is useful for highlighting important information, identifying patterns, and making your data easier to interpret.
How to Apply Conditional Formatting
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Click on Format in the menu.
- Select Conditional formatting.
- Define the rules and choose the desired formatting style.
- Click Done.
Conditional formatting is particularly useful for highlighting cells that meet certain criteria, such as sales targets, overdue dates, or top-performing categories.
CASE Function
UPPER, LOWER, PROPER Functions
These functions are used to change the case of text in cells, ensuring consistency and proper formatting.
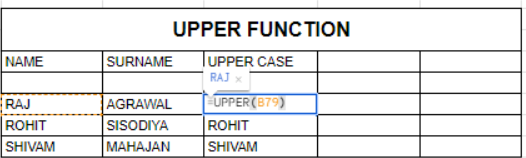
UPPER Function
The UPPER function converts all letters in a text string to uppercase.
- Syntax: =UPPER(text)
- Example: =UPPER(A1)
LOWER Function
The LOWER function converts all letters in a text string to lowercase.
- Syntax: =LOWER(text)
- Example: =LOWER(A1)
PROPER Function
The PROPER function capitalises the first letter of each word in a text string.
- Syntax: =PROPER(text)
- Example: =PROPER(A1)
These functions help in standardising text data, making it easier to read and analyse.
LEFT, MID, RIGHT Functions
The LEFT, MID, and RIGHT functions are used to extract substrings from a text string based on specified positions.
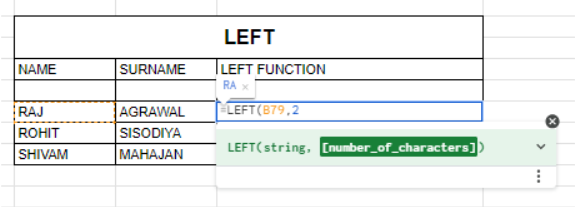
LEFT Function
The LEFT function extracts a specified number of characters from the beginning of a text string.
- Syntax: =LEFT(text, number_of_characters)
- Example: =LEFT(A1, 3)
MID Function
The MID function extracts a substring from a text string starting at a specified position.
- Syntax: =MID(text, start_position, number_of_characters)
- Example: =MID(A1, 4, 5)
RIGHT Function
The RIGHT function extracts a specified number of characters from the end of a text string.
- Syntax: =RIGHT(text, number_of_characters)
- Example: =RIGHT(A1, 3)
These functions are useful for parsing and extracting specific parts of text, such as IDs, names, or codes from a larger string.
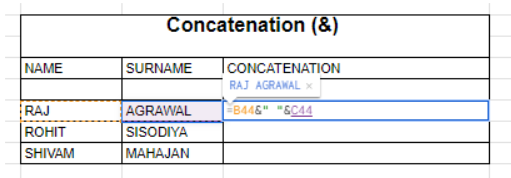
CONCATENATE Function
The CONCATENATE function joins multiple text strings into one.
- Syntax: =CONCATENATE(text1, text2, …)
- Example: =CONCATENATE(A1, ” “, B1)
TEXTJOIN Function
The TEXTJOIN function is similar to CONCATENATE but allows you to specify a delimiter and can ignore empty cells.
- Syntax: =TEXTJOIN(delimiter, ignore_empty, text1, text2, …)
- Example: =TEXTJOIN(“, “, TRUE, A1, B1, C1)
These functions are essential for combining data from different cells, making them useful for creating full names, addresses, and other combined data strings.
Conclusion
Text manipulation and conditional formatting are essential for organising, analysing, and visualising data in Google Sheets. By mastering techniques like conditional formatting, CASE function , LEFT, MID, RIGHT functions, CONCATENATE, and TEXTJOIN, you can ensure your data is clean, well-structured, and easily interpretable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Use the Conditional Formatting feature to define rules and apply formatting styles based on the contents of the cells.
Use the LEFT, MID, and RIGHT functions to extract substrings from a text string based on specified positions.
The CONCATENATE function joins multiple text strings into one, while the TEXTJOIN function allows you to specify a delimiter and can ignore empty cells.
By incorporating these techniques into your data management routine, you can enhance the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of your data, leading to more insightful and impactful analyses.

