Introduction
Java is an object-oriented programming language and object creation is a fundamental aspect of object-oriented programming. The new keyword in Java is an essential part of creating objects. The new keyword in Java is used to create objects, what happens when an object is created using the new Keyword in Java, and some important things to keep in mind when using the new Keyword in Java to create objects. We will also discuss some examples for a better understanding of the topic.
What is New Keyword in Java?
The new keyword in Java is used to create an instance of a class, also known as an object. It is used to allocate memory for an object and call the constructor of the class to initialize the object’s state.
The new keyword is followed by the constructor of a class, which sets the initial values for the object’s fields and performs any other necessary setup. The constructor is a special method that is called automatically when an object is created. Without the new keyword, an object cannot be created and the constructor cannot be called.
Syntax of new Keyword in Java
ClassName objName = new ClassName();
Process of Object Creation in Java
The process of object creation in Java involves several steps:
Declare a variable
A variable is declared with the class type of the object that needs to be created. The variable does not hold the object itself, but it holds the reference to the object.
Syntax
ClassName objName;Allocate memory
The new keyword is used to allocate memory for the object on the heap. The memory is reserved for the object’s fields and methods.
Syntax
ClassName objName = new ClassName();Initialize the object
The constructor of the class is called to initialize the object’s state. The constructor sets the initial values for the object’s fields and performs any other necessary setup.
here’s a simple Java code demonstrating the process of object creation:
// Define a class
class MyClass {
// Fields
int myField;
// Non-parameterized constructor
public MyClass() {
// Initialize fields or perform other setup
myField = 0;
}
// Parameterized constructor
public MyClass(int initialValue) {
// Initialize fields with parameter value
myField = initialValue;
}
// Method
public void display() {
System.out.println("Value of myField: " + myField);
}
}
public class ObjectCreationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Step 2: Instantiate the class using the new keyword and call constructor
MyClass obj1 = new MyClass(); // Non-parameterized constructor
// Step 4: Access object members
obj1.myField = 10; // Assigning a value to a field
obj1.display(); // Calling a method
MyClass obj2 = new MyClass(20); // Parameterized constructor
obj2.display(); // Calling a method
}
}
In this code:
- We define a class
MyClasswith a fieldmyField, two constructors (non-parameterized and parameterized), and a methoddisplay. - In the
ObjectCreationDemoclass:- We instantiate the
MyClassclass using both the non-parameterized and parameterized constructors. - We access the object members (field and method) using the object references (
obj1andobj2).
- We instantiate the
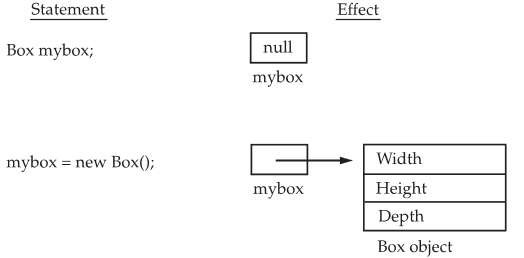
Here New allocates memory for an object during run time. The advantage of this approach is that your program can create as many or as few objects as it needs during the execution of your program. However, since memory is finite, it is possible that new will not be able to allocate memory for an object because insufficient memory exists.
Points to Remember about new Keyword in Java
Here are some important points to remember about the new keyword in Java:
- The new keyword in Java is used to create an instance of a class, also known as an object.
- The new keyword in Java is used to allocate memory for the object on the heap, the memory space where objects are stored.
Example
public class HeapAllocationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an instance of a class using the new keyword
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
// Accessing the object
obj.myMethod();
}
}
class MyClass {
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println("Object created and accessed successfully!");
}
}
Output
Object created and accessed successfully!
- The new keyword in Java calls the constructor of a class to initialize the object’s state. The constructor sets the initial values for the object’s fields and performs any other necessary setup.
Example
public class ConstructorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an instance of a class using the new keyword
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
// Accessing the object's state
obj.display();
}
}
class MyClass {
int myField;
// Constructor: called when an object is created with the new keyword
public MyClass() {
// Setting initial values for the object's fields
myField = 10;
}
// Method to display the object's state
public void display() {
System.out.println("Value of myField: " + myField);
}
}
Output
Value of myField: 10- The new keywords in Java also allows for dynamic memory allocation, it can be used to create arrays dynamically, which means the size of the array can be determined during runtime.
Example
public class DynamicArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Dynamically allocating memory for an array
int size = 5; // Size determined during runtime
int[] dynamicArray = new int[size];
// Initializing the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
dynamicArray[i] = i * 10;
}
// Accessing and displaying the array elements
System.out.println("Array elements:");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.println(dynamicArray[i]);
}
}
}
Output
Array elements:
0
10
20
30
40
- The new keywords in Java returns a reference to the object that was created, this reference can be stored in a variable and it can be used to access and interact with the object.
Example
public class NewKeywordReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an instance of a class using the new keyword
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
// Using the reference variable to access and interact with the object
obj.myMethod();
}
}
class MyClass {
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println("Object created and accessed successfully!");
}
}
Output
Object created and accessed successfully!- When creating an object with the new keywords in Java, the object is created on the heap, and it will remain in memory until it is no longer reachable by any reference in the code, at that point, it will be eligible for garbage collection.
What is the use of New Keyword in Java
Here are the some of uses of new keyword in Java:
- Memory Allocation: The new keywords is used to allocate memory for an object on the heap, the memory space where objects are stored in Java. Without the “new” keyword, an object cannot be created and there would be no memory allocated for it.
- Object Initialization: The new keyword in java also calls the constructor of a class to initialize the object’s state. The constructor sets the initial values for the object’s fields and performs any other necessary setup. Without the “new” keyword, the constructor cannot be called and the object would not be properly initialized.
- Object Polymorphism: The new keywords in java is used to create instances of subclasses that inherit from a superclass, the runtime type of the object will be the type of the subclass, making the object able to use the method overridden by the subclass and not the one inherited from the superclass.
- Dynamic Memory Allocation: the new Keywords in Java can be used to create arrays dynamically, which means the size of the array can be determined during runtime.
Conclusion
The new keywords in Java is used to create an instance of a class, also known as an object. It is used to allocate memory for an object on the heap and call the constructor of the class to initialize the object’s state. Each time the new keywords in Java is used, a new and unique instance of the class is created, which has its own state and behavior. It also plays a key role in polymorphism by allowing the creation of instances of subclasses that inherit from a superclass, and dynamic memory allocation by allowing the creation of arrays dynamically. The new keywords in Java is an essential part of object-oriented programming and allows for the creation and initialization of objects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: The new keyword in Java returns a reference to the new object that has been created.
Q2. What is the difference between static and new keyword in Java?
Ans: “new” is used to create a new instance of a class, while “static” is used to declare a variable or method that belongs to the class rather than to an instance of the class.
Q3. How many objects can be created using the new keyword in Java?
Ans: You can create as many objects as you need using the new keyword in Java.
Q4. What happens if you don’t use the new keyword in Java to create an object?
Ans: If you don’t use the new keyword in Java to create an object, then you will not have a valid reference to that object.
Q5. Can you create an object without using the new keyword in Java?
Ans: No, you cannot create an object without using the new keyword in Java.

