Introduction
Access modifiers in Java play a crucial role in controlling the accessibility of classes, methods, and variables within a program. Let’s illustrate their importance with a real-world example.
Imagine you’re developing a banking application. In this application, you have different classes representing various components such as accounts, transactions, and customers. Each of these classes has its own set of variables and methods, some of which need to be accessed from outside the class, while others should be kept private for internal use only.
Access modifiers in Java are keywords that are used to control the accessibility or visibility of classes, methods, and variables within a Java program. They determine which other classes can access a particular class, method, or variable.
Types of Access Modifiers in Java
There are four types of access modifiers available in Java:
- Default – No keyword required
- Private
- Protected
- Public
Default Access Modifier
The default access modifier in Java is used when no access modifier is explicitly specified. It provides package-level access, meaning that classes, methods, and variables with default access are accessible only within the same package.
Here’s a real-world example illustrating the default access modifier:
Let’s say you’re developing a library management system. You have a package library containing classes related to managing books, such as Book, Library, and Librarian. These classes have methods and variables that should only be accessed within the library package.
package library;
class Book {
String title;
String author;
int pages;
void displayInfo() {
System.out.println("Title: " + title);
System.out.println("Author: " + author);
System.out.println("Pages: " + pages);
}
}
// Library.java
package library;
class Library {
// Some methods and variables
}
// Librarian.java
package library;
class Librarian {
// Some methods and variables
}In this example, the classes Book, Library, and Librarian do not have an access modifier explicitly specified. Therefore, they have default access, which means they are accessible only within the library package. If you try to access these classes from outside the library package, you’ll get a compilation error.
Private Access Modifier
The private access modifier in Java restricts the access of a class member (variable or method) only to the class in which it is declared. Here’s a real-world example demonstrating the use of the private access modifier:
public class BankAccount {
private String accountNumber; // Private variable
private double balance; // Private variable
public BankAccount(String accountNumber) {
this.accountNumber = accountNumber;
this.balance = 0.0; // Initialize balance to 0
}
public void deposit(double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
balance += amount;
System.out.println(amount + " deposited into account " + accountNumber);
}
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (amount > 0 && amount <= balance) {
balance -= amount;
System.out.println(amount + " withdrawn from account " + accountNumber);
} else {
System.out.println("Insufficient funds");
}
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
// BankApp.java
public class BankApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankAccount account = new BankAccount("1234567890");
// We cannot directly access the private members of BankAccount
// account.accountNumber = "9876543210"; // Compilation error: accountNumber has private access in BankAccount
// account.balance = 10000; // Compilation error: balance has private access in BankAccount
// But we can interact with BankAccount using its public methods
account.deposit(500);
account.withdraw(200);
System.out.println("Current Balance: " + account.getBalance());
}
}In this example:
- The
BankAccountclass has two private variables,accountNumberandbalance. These variables are encapsulated within the class and can only be accessed and modified by methods within the same class. - The
BankAppclass cannot directly access the private variablesaccountNumberandbalanceof theBankAccountclass. Attempting to do so would result in a compilation error. - However,
BankAppcan interact with theBankAccountobject using its public methods such asdeposit,withdraw, andgetBalance. These methods internally access and modify the private variables of theBankAccountclass, maintaining data encapsulation and ensuring controlled access to sensitive data.
Protected Access Modifier
The protected access modifier in Java allows the member (variable or method) to be accessed within the same package or by subclasses, even if they are in different packages. Here’s a real-world example demonstrating the use of the protected access modifier:
Suppose we are building a simple system for a school. We have a superclass Person representing a person’s basic information, and subclasses Student and Teacher representing specific types of people in the school.
package school;
public class Person {
protected String name; // Protected variable
protected void introduce() { // Protected method
System.out.println("Hello, my name is " + name);
}
}
// Student.java
package school;
public class Student extends Person {
private int studentId; // Private variable
public Student(String name, int studentId) {
this.name = name; // Accessing protected member from superclass
this.studentId = studentId;
}
public void displayInfo() {
introduce(); // Accessing protected method from superclass
System.out.println("I am a student with ID " + studentId);
}
}
// Teacher.java
package school;
public class Teacher extends Person {
private String subject; // Private variable
public Teacher(String name, String subject) {
this.name = name; // Accessing protected member from superclass
this.subject = subject;
}
public void displayInfo() {
introduce(); // Accessing protected method from superclass
System.out.println("I am a teacher of " + subject);
}
}
// SchoolApp.java
package app;
import school.Student;
import school.Teacher;
public class SchoolApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student("John", 123);
student.displayInfo();
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Jane", "Math");
teacher.displayInfo();
}
}In this example:
- The
Personclass has a protected variablenameand a protected methodintroduce(). These members can be accessed by subclasses such asStudentandTeacher. - The
StudentandTeacherclasses extend thePersonclass, allowing them to inherit the protected members. - Both
StudentandTeacherclasses use thenamevariable andintroduce()method from thePersonsuperclass. - The
SchoolAppclass creates instances ofStudentandTeacherand calls their respectivedisplayInfo()methods, which internally use the protected members inherited from the superclassPerson.
Public Access Modifier
The public access modifier in Java allows a class, method, or variable to be accessible from any other class, regardless of the package it belongs to. Here’s a real-world example demonstrating the use of the public access modifier:
package library;
public class Book {
public String title;
public String author;
public int pages;
public void displayInfo() {
System.out.println("Title: " + title);
System.out.println("Author: " + author);
System.out.println("Pages: " + pages);
}
}
// Library.java
package library;
public class Library {
public void addBookToCatalog(Book book) {
// Logic to add the book to the library catalog
}
}
// LibraryApp.java
package app;
import library.Book;
import library.Library;
public class LibraryApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an instance of Book and accessing its public members
Book book = new Book();
book.title = "Java Programming";
book.author = "John Doe";
book.pages = 300;
book.displayInfo();
// Creating an instance of Library and calling its public method
Library library = new Library();
library.addBookToCatalog(book);
}
}In this example:
- The
Bookclass has its attributes (title,author,pages) and method (displayInfo()) declared with thepublicaccess modifier. This allows them to be accessed from any other class. - The
Libraryclass has a methodaddBookToCatalog(Book book)with thepublicaccess modifier, allowing it to be accessed from any other class. This method accepts aBookobject as a parameter, demonstrating how public access allows interaction between different classes. - The
LibraryAppclass in a different packageappcan create instances ofBookandLibraryand interact with their public members. It demonstrates how classes from different packages can accesspublicmembers of other classes.
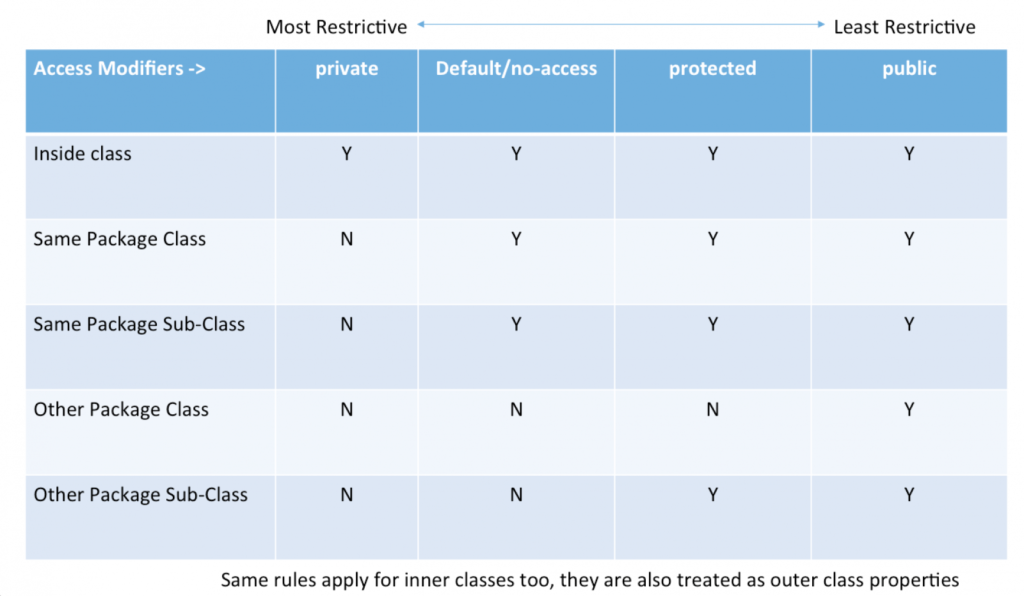
Understanding Java Access Modifiers
Algorithm to Use Access Modifier in Java
The following steps can be followed to choose an appropriate access modifier based on the desired level of visibility.
- Determine the scope of the variable or method that needs to be accessed.
- Use the public access modifier if the variable or method needs to be accessible from anywhere in the program, including outside classes.
- Use the protected access modifier if the variable or method needs to be accessible within the same package or subclass but not outside the package or subclass.
- Use the default (package-private) access modifier if the variable or method needs to be accessible within the same package only.
- Use the private access modifier if the variable or method needs to be accessible only within the same class.
Conclusion
Access modifiers in Java provide a powerful mechanism for controlling the visibility and accessibility of classes, methods, and variables within a program. By specifying the appropriate access modifier, developers can enforce encapsulation, data hiding, and code organization, leading to more maintainable and secure code.
The public access modifier allows entities to be accessible from any other class, protected grants access within the same package and by subclasses, default (package-private) restricts access to within the same package, and private limits access to within the same class. Each access modifier serves specific purposes in managing the interactions between different components of a Java program, promoting good software design practices and facilitating code reuse.
Frequently Asked Questions
Access modifiers are keywords in Java that define the accessibility or visibility of classes, methods, and variables within a program.
There are four types of access modifiers in Java: public, protected, default (package-private), and private.
public access modifier do? The public access modifier makes the class, method, or variable accessible from any other class, regardless of the package it belongs to.
public method access private variables of its class? Yes, a public method in a class can access and modify private variables of the same class.

