If Statement
Understanding if else in Python. Sometimes the programmer needs to check the evaluation of certain expression(s), whether the expression(s) evaluate to True or False. If the expression evaluates to False, then the program execution follows a different path then it would have if the expression had evaluated to True.
Based on this, the conditional statements are further classified into following types; if, if……else, elif, nested if.
If Statement in Python
A simple if statement works on following principle,
- execute the block of code inside if statement if the expression evaluates True.
- ignore the block of code inside if statement if the expression evaluates False and return to the code outside if statement.
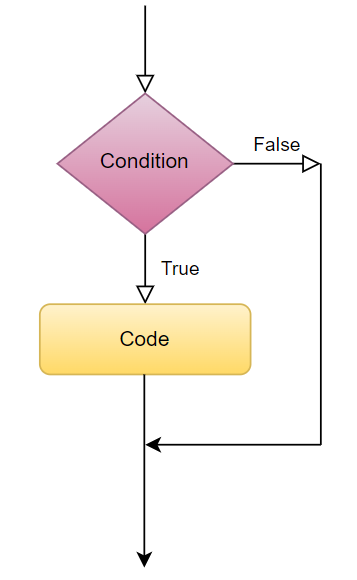
Example:
applePrice = 180
budget = 200
if (applePrice <= budget):
print("Alexa, add 1kg Apples to the cart.")Output:
Alexa, add 1kg Apples to the cart.If-Else Statement
An if……else statement works on the following principle,
- execute the block of code inside if statement if the expression evaluates True. After execution return to the code out of the if……else block.
- execute the block of code inside else statement if the expression evaluates False. After execution return to the code out of the if……else block.
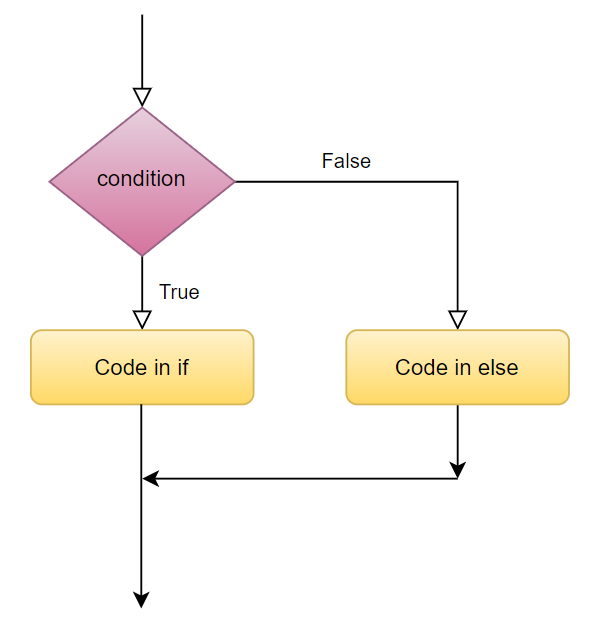
If-Else Statement Example:
applePrice = 210
budget = 200
if (applePrice <= budget):
print("Alexa, add 1kg Apples to the cart.")
else:
print("Alexa, do not add Apples to the cart.")Output:
Alexa, do not add Apples to the cart.Age Verification:
age = 17
if age >= 18:
print("You are eligible to vote.")
else:
print("You are not eligible to vote yet.")This code checks whether a person’s age is 18 or above. If the age is 18 or greater, it informs the person that they are eligible to vote; otherwise, it informs them that they are not yet eligible.
Discount Calculation
total_amount = 150
discount_threshold = 100
if total_amount >= discount_threshold:
discount = 0.1 * total_amount # 10% discount
final_amount = total_amount - discount
print(f"You qualify for a 10% discount. Your final amount is ${final_amount}.")
else:
print("Sorry, you need to spend more to qualify for a discount.")In this example, if the total_amount is greater than or equal to the discount_threshold, a 10% discount is applied; otherwise, it informs the customer that they need to spend more to qualify for a discount.
Conclusion
The if else statement in Python is fundamental for building conditional logic in your programs. It allows you to control the flow of execution based on specific conditions. By mastering the if else statement, you can create powerful algorithms and applications that respond dynamically to different scenarios. Remember to write clear and concise conditions, and always test your code with various inputs to ensure it behaves as expected. With practice, you’ll become proficient in using if else statements to solve a wide range of programming problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: The if statement is used to make decisions in Python programs. It allows you to execute a block of code only if a specified condition is true.
Q2. What is the syntax of the if statement?
Ans: The basic syntax is: pythonCopy code if condition: # code block to execute if the condition is true
Q3. What is the else statement used for?
Ans: The else statement is used in conjunction with the if statement to execute a block of code if the if condition is false.
Q4. Can I have multiple conditions using elif?
Ans: Yes, you can use elif (short for “else if”) to specify additional conditions to check if the initial if condition is false.
Q5. What happens if multiple conditions are true?
Ans: In Python, only the block of code associated with the first true condition encountered will be executed. Subsequent elif and else blocks are skipped.
Q6. Can I nest if statements within each other?
Ans: Yes, you can nest if statements within each other to create more complex decision-making structures.
Q7. What are common mistakes to avoid when using if else statements?
Ans: Forgetting the colon : after the if and else statements. Misunderstanding the logic leading to incorrect conditions. Forgetting indentation, which is crucial in Python to define the scope of code blocks.

