Introduction
Google Sheets is an indispensable tool that provides a wide range of functions to help users manage and analyze data efficiently. By understanding and utilizing these functions, you can significantly enhance your productivity. In this guide, we will explore essential arithmetic and logical formulas, provide an overview of functions, explain the autofill feature, and delve into specific functions such as “IF,” “IFS,” “SUM,” and “COUNT.”
Overview of Functions in Google Sheets
Functions in Google Sheets are predefined formulas designed to perform calculations using specific values (arguments) in a particular order. These functions can handle a variety of tasks, from simple arithmetic operations to complex data analysis.
Arithmetic, Logical and Comparison Operators
Arithmetic operators are used for basic mathematical operations, while logical operators help evaluate conditions and return specific results based on those conditions and Comparison operators help compare with the given value.
Basic Arithmetic Operators
- Addition (+): Adds two or more numbers.
- Example: =A1 + B1
- Subtraction (-): Subtracts one number from another.
- Example: =A1 – B1
- Multiplication (*): Multiplies two or more numbers.
- Example: =A1 * B1
- Division (/): Divides one number by another.
- Example: =A1 / B1
Logical Operator
- AND: Returns TRUE if all the specified conditions are TRUE.
- Condition: A1 is greater than 0 and B1 is Less than 10
- Example: =AND(A1 > 0, B1 < 10)
- OR: Returns TRUE if any of the specified conditions are TRUE.
- Condition: A1 is greater than 0 or B1 is Less than 10
- Example: =OR(A1 > 0, B1 < 10)
- NOT: Returns the opposite of the given condition.
- Condition: A1 is not less than 0
- Example: =NOT(A1 > 0)
Comparison Operators
- Equal to (=)
- Checks if the values in two cells are identical.
- Example: =A1 = B1
- Not equal to (<>)
- Determines if the values in two cells are different.
- Example: =A1 <> B1
- Greater than (>)
- Checks if the value in one cell is greater than the value in another cell.
- Example: =A1 > 85
- Less than (<)
- Determines if the value in one cell is less than the value in another cell.
- Example: =A1 < B1
- Greater than or equal to (>=)
- Checks if the value in one cell is greater than or equal to the value in another cell.
- Example: =A1 >= B1
- Less than or equal to (<=)
- Determines if the value in one cell is less than or equal to the value in another cell.
- Example: =A1 <= B1
Text Concatenation Operator
Concatenation (&)
- Join two or more text strings into one string.
- Example: =A1 & ” ” & B1 (This combines the contents of cell A1 and B1 with a space in between.)
Autofill in Google Sheets
Autofill is a powerful feature that allows you to quickly fill cells with repetitive or sequential data. This feature can save you time by automatically completing a series (such as dates or numbers) or copying the content of one cell to adjacent cells.
How to Use Autofill
- Enter the initial data in a cell or a range of cells.
- Select the cell or range, then drag the fill handle (a small square at the bottom-right corner of the selection) across the cells you want to fill.
- Release the mouse button to autofill the selected cells.
The “IF” and “IFS” Functions
The “IF” function is commonly used in Google Sheets to perform logical tests and return one value if the condition is TRUE and another if it is FALSE. The “IFS” function evaluates multiple conditions and returns a value corresponding to the first TRUE condition.
IF Function
This function checks if a condition is met and returns one value if true and another if false.
- Syntax: =IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false)
- Example: =IF(A1 > 10, “High”, “Low”)
IFS Function
This function evaluates multiple conditions and returns a value for the first true condition.
- Syntax: =IFS(condition1, value1, condition2, value2, …)
- Example: =IFS(A1 > 90, “A”, A1 > 80, “B”, A1 > 70, “C”, TRUE, “F”)
SUM Functions
The SUM functions allow you to add up a range of numbers.
SUM
- Syntax: =SUM(range)
- Example: =SUM(A1:A10)
SUMIF
- Syntax: =SUMIF(range, criterion, [sum_range])
- Example: =SUMIF(A1:A10, “>10”, B1:B10)
COUNT Functions
The COUNT function is used to count the number of cells that contain numerical data within a specified range.
COUNT: Only counts cells with numerical data.
- Syntax: =COUNT(range)
- Example: =COUNT(A1:A10)
COUNTA
The COUNTA function is used to count the number of non-empty cells within a specified range, regardless of the type of data they contain.
COUNTA: Counts cells with any type of data (numbers, text, dates, etc.).
- Syntax: =COUNTA(range)
- Example: =COUNTA(A1:A10)
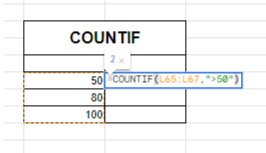
COUNTIF
- Syntax: =COUNTIF(range, criterion)
- Example: =COUNTIF(A1:A10, “>10”)
Conclusion
Google Sheets offers a comprehensive set of functions that can simplify your data management and analysis tasks. By mastering arithmetic and logical formulas, the autofill feature, and essential functions like IF, IFS, SUM, and COUNT, you can greatly enhance your productivity and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
The SUM function adds all the numbers in a specified range, while the SUMIF function adds only the numbers that meet a specific criterion.
The IF function evaluates a single condition and returns one of two values based on whether the condition is TRUE or FALSE. The IFS function evaluates multiple conditions and returns the value corresponding to the first TRUE condition.
Yes, you can combine logical functions like AND and OR with the IF function to create more complex logical tests.
By learning these functions and techniques, you can become more efficient in managing and analysing your data. Happy spreadsheeting!

