Introduction
In CSS, the z-index property determines the stacking order of positioned elements along the z-axis (the axis perpendicular to the screen). It controls which elements appear in front of or behind other elements on a webpage. Here’s a concise overview:
- Stacking Context: The
z-indexproperty only applies to elements with apositionvalue ofrelative,absolute, orfixed. When elements overlap, thez-indexvalue determines their stacking order within their stacking context. - Higher Values: Elements with a higher
z-indexvalue are stacked above elements with lowerz-indexvalues within the same stacking context. If two elements have the samez-index, the one that comes later in the HTML source order is displayed on top. - Negative Values: Negative
z-indexvalues are allowed and can be used to place an element behind its stacking context. Elements with negativez-indexvalues are stacked below elements with zero or positivez-indexvalues within the same stacking context.
img {
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
z-index: -1;
}Example
<html>
<head>
<style>
.container {
position: relative;
}
.black-box {
position: relative;
border: 2px solid black;
height: 100px;
margin: 30px;
}
.gray-box {
position: absolute;
background: lightgray;
height: 60px;
width: 70%;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
.green-box {
position: absolute;
background: lightgreen;
width: 35%;
left: 270px;
top: -15px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
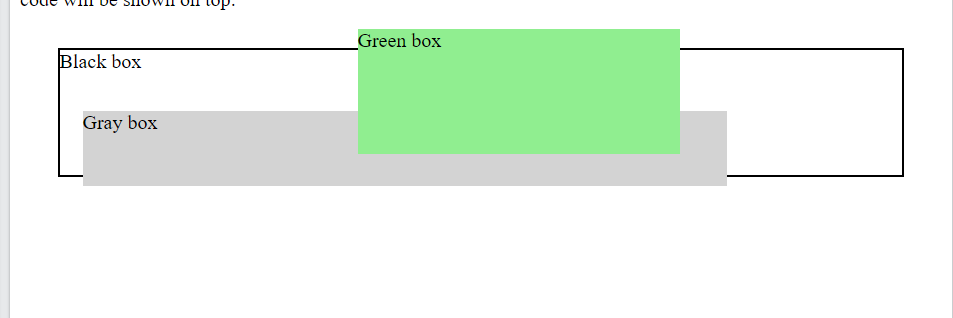
<div class="black-box">Black box</div>
<div class="gray-box">Gray box</div>
<div class="green-box">Green box</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output
Conclusion
In conclusion, z-index is a crucial CSS property for controlling the stacking order of elements on a webpage. By assigning different z-index values to positioned elements, developers can control their visual hierarchy and ensure elements appear in the desired order on the z-axis. Understanding how z-index works and its interaction with stacking contexts is essential for creating complex layouts and resolving stacking order issues in web development projects. While z-index provides powerful control over element stacking, it’s important to use it judiciously and with careful consideration to avoid unintended consequences and maintain a clear and intuitive visual hierarchy in the user interface.
Frequently Asked Questions
z-index is a CSS property that controls the stacking order of elements along the z-axis. Elements with higher z-index values are stacked above elements with lower values within the same stacking context.
No, z-index only applies to elements with a position value of relative, absolute, or fixed. These elements create a stacking context and z-index determine their stacking order within that context.
If two elements have the same z-index value, the one that comes later in the HTML source order will be displayed on top.
Yes, negative z-index values are allowed. They can be used to place an element behind its stacking context or other elements with zero or positive z-index values within the same stacking context.
To debug z-index issues, you can inspect elements using developer tools in your browser. Check the z-index values of the elements involved and ensure they’re positioned correctly within their stacking contexts. Adjust z-index values as needed to achieve the desired stacking order.

