Introduction
CSS padding is a fundamental concept in web design that defines the space between an element’s content and its border. It provides internal spacing within an element, allowing designers to control the distance between the content and the border edges.
Key Points
- Purpose: Padding is used to create space inside an element, separating its content from the border. It enhances readability and visual appeal by providing breathing room around the content.
- Setting Padding: Padding can be set using the
paddingproperty in CSS. This property accepts values in pixels, ems, rems, percentages, or keywords likeauto. You can set padding for all four sides simultaneously or individually for each side usingpadding-top,padding-right,padding-bottom, andpadding-left. - Individual Side Padding: You can specify different padding values for each side of an element using individual padding properties. For example,
padding-top: 10px;sets a padding of 10 pixels for the top side of the element. - Interaction with Layout: Padding affects the overall size of an element, adding to its dimensions. When setting the
widthandheightof an element, padding is included in the total size by default. However, you can adjust this behavior using thebox-sizingproperty. - Visual Representation: Padding is visually represented as the space between the content and the border of an element. It can be styled with different colors or backgrounds to enhance the visual appearance of the element.
div {
width: 300px;
padding: 25px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
Output
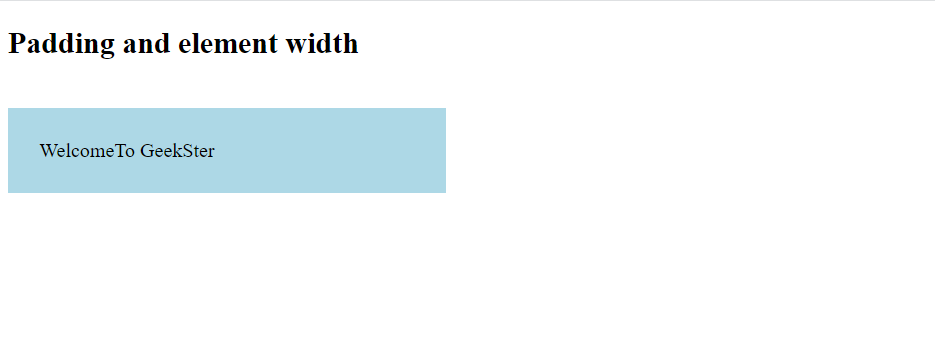
Padding – Shorthand Property
To shorten the code, it is possible to specify all the padding properties in one property.
The padding property is a shorthand property for the following individual padding properties:
padding-toppadding-rightpadding-bottompadding-left
So, here is how it works:
If the padding property has four values:
- padding: 25px 50px 75px 100px;
- top padding is 20px
- right padding is 50px
- bottom padding is 65px
- left padding is 100px
div {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 20px 50px 65px 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
}Output

- padding: 25px 50px 75px;
- top padding is 25px
- right and left paddings are 50px
- bottom padding is 75px
- padding: 25px 50px;
- top and bottom paddings are 25px
- right and left paddings are 50px
Conclusion
CSS padding is a critical component of web design, providing designers with the ability to control the spacing between an element’s content and its border. Through careful manipulation of padding values, designers can enhance the visual appeal and readability of web pages, creating well-structured layouts that engage users effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
CSS padding is the space between the content of an element and its border. It provides internal spacing, allowing designers to control the distance between the content and the border of an element.
Padding can be set using the padding property in CSS. It accepts values in pixels, ems, rems, percentages, or keywords like auto. You can specify padding for all four sides simultaneously or individually for each side using padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom, and padding-left.
Yes, you can specify different padding values for each side of an element using individual padding properties like padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom, and padding-left.
Padding increases the total size of an element, pushing its content away from the border. It is useful for creating spacing between the content and the border, enhancing readability and visual appeal.
Padding: Space between the content area and the border of an element.
Margin: Space outside the border, determining the distance between the element and its neighboring elements.

