In web design, CSS font play a crucial role in defining the visual appearance of text content on web pages. CSS provides various properties to control the font family, size, weight, style, and other aspects of text rendering, allowing designers to create visually appealing and readable typography.
Key Features of CSS Fonts
1.Font Family
The font-family property specifies the font family for text content. It allows designers to choose from a wide range of typefaces, including system fonts and custom web fonts. Multiple font families can be specified as fallback options in case the preferred font is not available.
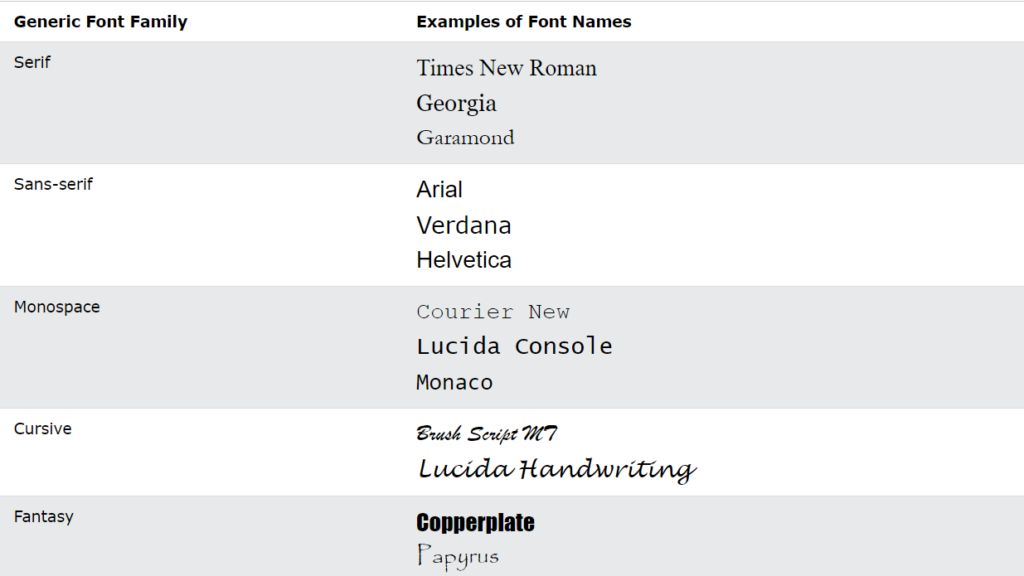
In CSS there are five generic font families:
- Serif fonts have a small stroke at the edges of each letter. They create a sense of formality and elegance.
- Sans-serif fonts have clean lines (no small strokes attached). They create a modern and minimalistic look.
- Monospace fonts – here all the letters have the same fixed width. They create a mechanical look.
- Cursive fonts imitate human handwriting.
- Fantasy fonts are decorative/playful fonts.

Font Examples
2.Font Size
The font-size property sets the size of the font. It can be specified in pixels, ems, rems, percentages, or other relative units. Font size affects the overall legibility and visual hierarchy of text content on the webpage.
The font size value can be an absolute, or relative size.
Absolute size:
- Sets the text to a specified size
- Does not allow a user to change the text size in all browsers (bad for accessibility reasons)
- Absolute size is useful when the physical size of the output is known
Relative size:
- Sets the size relative to surrounding elements
- Allows a user to change the text size in browsers
If you do not specify a font size, the default size for normal text, like paragraphs, is 16px (16px=1em).
h1 {
font-size: 40px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 30px;
}
p {
font-size: 14px;
}Output

3.Font Weight
The font-weight property determines the thickness or boldness of the font. It accepts values ranging from 100 (thin) to 900 (bold), as well as keywords like normal and bold.
p.normal {
font-weight: normal;
}
p.thick {
font-weight: bold;
}Output

4.Font Style
The font-style property controls the style of the font, allowing designers to make text italic or normal. It accepts values like italic, oblique, and normal.
p.normal {
font-style: normal;
}
p.italic {
font-style: italic;
}
p.oblique {
font-style: oblique;
}output

CSS Font Property
To shorten the code, it is also possible to specify all the individual font properties in one property.
The font property is a shorthand property for:
font-stylefont-variantfont-weightfont-size/line-heightfont-family
p.a {
font: 20px Arial, sans-serif;
}
p.b {
font: italic small-caps bold 12px/30px Georgia, serif;
}Output:
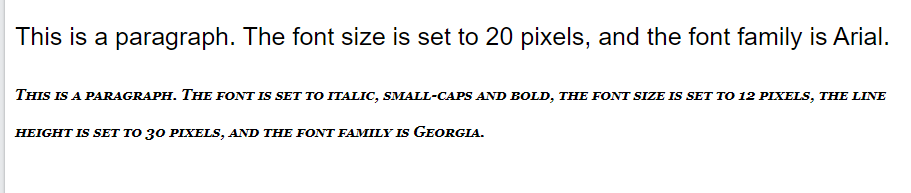
Conclusion
CSS fonts are essential for controlling the typography and visual appearance of text content on web pages. By leveraging CSS font properties, designers can choose appropriate typefaces, adjust font sizes and weights, apply styles and decorations, and transform text content to enhance readability and visual appeal. Mastery of CSS fonts empowers designers to create cohesive and visually engaging web designs that effectively communicate with users.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans – You can specify a custom font in CSS using the font-family property. If the custom font is hosted on your server, you can use the @font-face rule to define it and then use its name in the font-family property.
Q -2 Can I use multiple fonts in CSS?
Ans – Yes, you can specify multiple font families in the font-family property separated by commas. The browser will use the first available font in the list.
Q -3 How do I ensure fallback fonts in case the preferred font is not available?
Ans – You can specify fallback fonts in the font-family property after the preferred font family. If the preferred font is not available, the browser will use the first available fallback font.
Q -4 How can I set the size of the font in CSS?
Ans – The size of the font can be set using the font-size property. You can specify the size in pixels, ems, rems, percentages, or other relative units.

